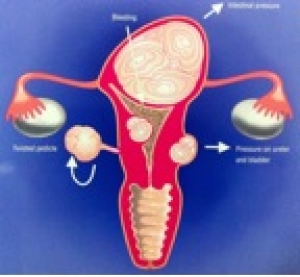
This is the most common benign tumor of the uterus , affecting 1 in 5 women. A departure from the muscular wall of the uterus , can be single or, as is more frequently multiple. Its volume is very variable from a small grain of wheat to a mass that occupies part of the abdomen.
The growth of fibroids is usually slow and gradual , but sometimes , in a relatively short time , there may be a rapid growth, this can occur during pregnancy, or after 40 years.
Symptoms related to the presence of a fibroid
Often the fibroid is not from no symptoms .
A fairly common symptom is heavy menstruation , present in about half of women who have fibroids. Another symptom may be due to the pack size and compression of neighboring organs when the fibroid has a large volume, more than 8-10 cm.
The mere presence of the fibroid does not mean need for surgery . We operate only the fibroids that their volume or their position bother to nearby organs or cause bleeding can not be controlled with medical treatment.
Diagnosis
For the diagnosis we make use of the gynecological examination and imaging techniques such as ultrasound and hysteroscopy .
Ultrasound can detect fibroids who do not feel the visit , provide information on the number, size and location of the same.
Hysteroscopy allows you to assess how the fibroid imprints , or come into the uterine cavity , if intracavitary fibroids too small may cause cycles very abundant.
Therapy
The therapeutic approach depends on the age of the woman, or the entity of the development of fibroids , from having completed his family and the presence of symptoms attributable to the fibroid .
If the patient does not present any symptoms, the doctor's attitude is to control the framework with a clinical examination and ultrasound every 6-12 months.
The use of a surgical therapy is justified in cases where the fibroid involves bleeding that does not respond to any medical treatment , or when , because of its size and position , squeeze or move to nearby organs (bowel , bladder, and rectum) , or exceed the volume of a uterus in the fourth month of pregnancy.
The surgical procedure may involve simple or removal of fibroids with preservation of the uterus ( myomectomy is defined ), or the complete removal of the uterus ( hysterectomy is defined ) or the uterine body , leaving only the neck ( you define hysterectomy subtotal ).
For shapes intracavitary removal is practiced for hysteroscopic , resection or vaporisation .
The choice of the type of surgery, conservative or demolition , is related to subjective factors such as the age of the patient , the desire to preserve reproductive function or at least to preserve the integrity of their genitalia , and objective factors that is linked to the characteristics of the fibroid , to its removable so , to the symptomatology , because the therapeutic choice must be able to ensure with sufficient safety for the resolution of the symptom which has been proposed.
READ ALL PATHOLOGIES


 Robotic surgery
Robotic surgery