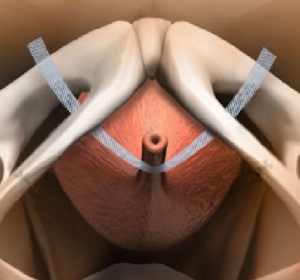
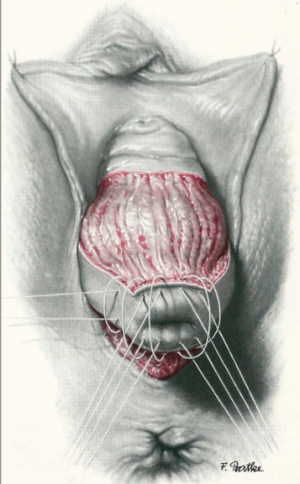
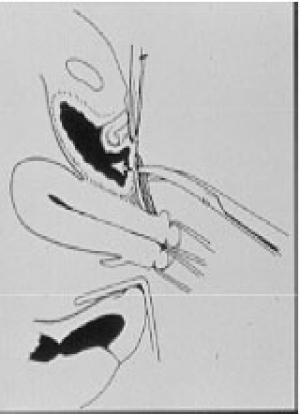
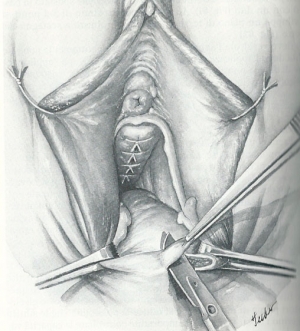
The vaginal surgery is a technique exclusive prerogative of gynecological surgery , as the same are carried out numerous actions that affect the female genital using a natural orifice present in women, ie the vagina.
The vagina is then incised and, through this incision , we enter the abdominal cavity being able to surgically treat various pathologies of the uterus, bladder and uterine adnexa .
Surgery for vaginal route not only involves less risk than the abdominal route but is also generally preferred by patients because it is less invasive . Indeed surgery by vaginal allows a more rapid postoperative recovery , causing less pain , less recovery time , and also leaves no visible scars , aspect that is of great importance from the aesthetic point of view .
The obese patients or those with respiratory and / or cardiac and / or blood coagulation disorders are preferably made ??by the vaginal route . In contrast, patients with problems in the hip joints and the spine and / or with very limited vaginal access can find contraindications in this surgical way . Possible intraoperative complications are represented by bleeding, perforation of the pelvic organs ( vecica and intestine) and the impossibility of extraction of the uterus. Among the postoperative complications can occur bleeding, infection , and fistula formation .
The surgeries that can be performed more frequently for the vaginal route are the following :
Hysterectomy + / - removal of appendages: the ovaries and fallopian tubes ( ie hysterectomy without removal of the uterus ) .
Correction of genital prolapse (bladder, uterus, rectum) through fascial repair with or without prosthesis prosthesis : cystopexy , uretropessi , rettopessi , colpoperineoplastica , without suspension , colpocleisi .
Correction of stress urinary incontinence : sling sottouretrali through placement of TVT , TOT .
There are also minor procedures that can be performed by the vaginal route :
Examination of the uterine cavity or diagnostic curettage ( curettage )
Plastic of the vulva and vagina
Removal of cysts of Naboth
Biopsy of the cervix uteri
Cone biopsy ( conization )
incision of the hymen
Removal of cysts and abscesses of Bartholin's gland
hysteroscopy
The vaginal surgery may be followed in spinal anesthesia ( ie a loco-regional anesthesia which provides that anesthetize only the lower part of the body) . It therefore avoids the woman all the risks associated with general anesthesia and also what contributes to a faster postoperative recovery of the patient. Usually the patients after surgery have time to recover fairly quickly, typically being able to get out of bed the same evening. The recovery of intestinal motility usually occurs within 24-48 hours.
READ ALL ACTIVITY


 Robotic surgery
Robotic surgery