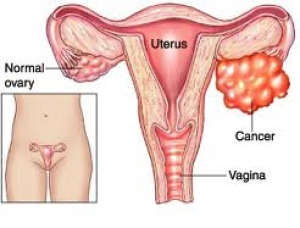
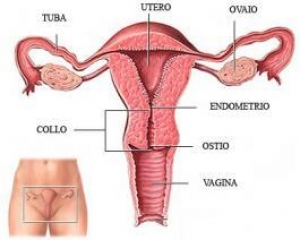
The ovaries are two organs of the size of about three inches (but with variations with respect to age ) located a right and a left to the uterus they are connected to the fallopian tubes.
Their are two functions : to produce eggs and female sex hormones , female reproductive cells .
Each month, when the woman is fertile and not pregnant , the ovaries produce an egg moves toward the uterus to be fertilized.
The ovarian cancer is due to the uncontrolled proliferation of cells of the organ, most of the time to departure from the epithelial cells (ie not from those that produce the ova ) . Although germ cells , however, can be the cause of a form of cancer .
Types
Aside from benign tumors , such as ovarian cysts , malignant tumors of the ovary are of three types: epithelial tumors , germ cell tumors and stromal tumors .
The epithelial tumors originate from epithelial cells that line the surface of the ovaries. They constitute more than 90 percent of malignant ovarian tumors .
The germ cell tumors originate from germ cells (those that give rise to ova ) and represent about 5 percent of malignant ovarian tumors are almost exclusive young age ( childhood and adolescence ) and can be differentiated from other malignant ovarian tumors because they produce tumor markers found in the blood ( such as alfaproteina or chorionic gonadotropin ) different from those produced by tumors of epithelial origin .
Stromal tumors originate from the gonadal stroma ( supporting tissue of the ovary ) . In theory, constitute a group easily diagnosed because the symptoms common to all ovarian tumors combine hormonal effects (ie, related to an excessive production of both male and female hormones , because part of the cell is able to produce testosterone ) . The majority of these tumors are characterized by a low malignancy. They account for about 4 percent of malignant ovarian tumors .
Evolution
Unfortunately, ovarian cancer shows no sign of him until it has reached considerable size and this heavily influences the outcome of care.
In the initial stages , ie, when the tumor is located in an ovary or even both , the result of adequate treatment is satisfactory. According to the 2006 Annual Report of the FIGO (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics) in the early stages (stage I ), the five-year survival is 85 per cent, so it is in the advanced stages in which the five-year survival drops 50-30 percent .
Symptoms
Ovarian cancer has no symptoms in the early stages . For this reason it is difficult to identify it early.
There are three symptoms that women should keep in mind as a possible early indicators of the presence of ovarian cancer : swollen abdomen , bloating , frequent need to urinate .
The claim several studies have appeared in recent years in medical journals .
According to experts, it is often overlooked as symptoms common to other minor illnesses .
Of course, to be considered only if you have (or in rapid sequence ) together and suddenly, in all other cases are not significant. These symptoms should be added to the feeling of satiety even on an empty stomach . When you experience these real alarm bells , it is good to ask the gynecologist a simple pelvic ultrasound , which can give an important indication diagnostics.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by pelvic examination ie pelvic examination and palpation of the abdomen.
Are important in the clinical assessment of the patient's age , size and texture of the ovaries.
Childbearing age the normal ovary measures 3.5 cm . Menopausal ovary undergoes atrophy , it measures 2 cm and late menopause less than 2 cm . If so palpable ovary in a woman of childbearing is a normal ovary , it is a cancer of the ovary in a postmenopausal woman is not necessarily malicious , but never dysfunctional . Therefore in menopausal and post- menopausal age the presence of a palpable ovary is presumptively a neoplasm , as well as childbearing age an ovary with a diameter greater than 3.5 cm and of a firm consistency . In these cases, you need a finer assessment .
The best transvaginal or transabdominal ultrasound is very useful, sometimes combined with the dosage of CA 125 , a serum marker whose values ??can be high , however, in many situations both gynecological and non- gynecological cancer , both in non-neoplastic diseases such as chronic liver disease, pancreatitis .
Besides ultrasound , are used CT abdomen , barium enema with barium and magnetic resonance imaging with the aim to check the spread of the tumor and the presence of metastases in the abdominal cavity . In general , as mentioned above, the pelvic exam , the determination of the level of CA 125 and transvaginal ultrasound offer any chance of an early diagnosis of ovarian cancer , but it does not give sufficient guarantees to be extended as screening of all the female population.
This approach is recommended in the small number of patients with ovarian cancer family type and should be performed every six months from the age of 30-35 years.
How to care
Women suffering from ovarian cancer undergo surgery. In the early stages may be feasible depending on the circumstances a minimally invasive surgery ( laparoscopy, single port , robotics ), while in the later stages , in order to remove all visible disease , it is almost always necessary to open surgery . The standard treatment requires: peritoneal washing , total hysterectomy , oophorectomy , peritoneal biopsies , appendectomy , and lymphadenectomy possible that tumor debulking surgery can mean extending the intestine, diaphragm , spleen, omentum . Ovarian cancer may also require the use of chemotherapy that is all the more important the more advanced the cancer is removed . One speaks of adjuvant chemotherapy (performed after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells in the body) or neoadjuvant (when it is carried out before the operation to reduce the mass of the tumor and make it more easily operable ) , in this case a diagnostic laparoscopy can help you decide the treatment of first instance : demolitive intervention vs. chemotherapy. There are many schemes : one of the most widely used is based on paclitaxel and cisplatin or carboplatin.
Radiation therapy is rarely used in the treatment of ovarian cancer if not for palliation of certain metastatic sites . We are studying different biological drugs for the treatment of ovarian cancer at an advanced stage : they are mostly still in the testing of substances on which they have high hopes for the future. The drug is the most studied cetuximab , which could slow down the progression of some forms of EGFR receptor positive .
Who is at risk
Among the risk factors for cancer of the ovary is the age , as evidenced by the fact that the majority of cases is identified after entering menopause , between the end of the fifth and sixth decade of life , being the peaks between 50 and 69 years.
Other risk factors are the length of the ovulatory period ie menarche ( first menstruation ) early , late menopause and not having children . Having had more children, breastfeeding and the long-term use of estrogen-progestin contraceptives decrease the risk of developing ovarian cancer and are therefore protective factors .
But there is another risk factor , and this consists of specific alterations of genes. According to an estimate by the National Cancer Institute a percentage between 7 and 10 percent of all cases is the result of a genetic alteration that has been handed down through the generations . In the presence of substantial genetic defects in the genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation can be present simultaneously or at different times of ovarian cancer and breast cancer. In these cases, cancer of the ovary occurs at a younger age than not tied to genetic alteration .
It should be noted, however, that the existence of ovarian cancer in the family does not provide the certainty that it will recur in all women related , but only that the latter have a higher risk than the general population . In cases belonging to families with high presence of ovarian cancer or breast cancer may be useful to a genetic test to determine the risk of the individual. And if the subject was a carrier of a genetic mutation should be adopted a program of close supervision with mammograms and ultrasounds .
Identifying genetic risk
Approximately one in ten cases of ovarian cancer is due to genetic defects.
More cases of the same tumor or two tumors associated with the same genetic alteration (as in the ovary and breast ) in the same branch of the family can raise the suspicion of inherited genetic alteration .
Unlike the case in which the disease is triggered by inappropriate lifestyle present in the whole family. In the first case it may be useful to consult a specialized genetic counseling center at a national cancer institute
How widespread is
In Italy, ovarian cancer affects around 4,000 women each year. It ranks ninth among the cancers , and constitutes 2.9 percent of all cancer diagnoses .
In Europe accounts for 5 percent of all female cancers . It is more common in the Caucasian population , in the countries of northern and western U.S. , much less common in Asian, African , South American .
Prevention
There are currently no scientifically reliable screening programs for the prevention of ovarian cancer.
Nevertheless, some studies have shown that an annual visit to the gynecologist performing the bimanual palpation of the ovary and transvaginal ultrasound monitoring can facilitate early diagnosis .
Some studies have attempted to use a program for screening healthy population of a marker in the blood , the CA 125 , but at the moment it is not reliable because too little specific . This marker is instead very useful in monitoring the eventual recovery of the disease in people suffering from ovarian cancer earlier.
READ ALL PATHOLOGIES


 Robotic surgery
Robotic surgery